AI-driven fusion of multimodal data for Alzheimer’s disease biomarker assessment
Aug 1, 2025·,,,,,,·
0 min read
Varuna H. Jasodanand
Sahana S. Kowshik
Shreyas Puducheri
Michael F. Romano
Lingyi Xu
Rhoda Au
Vijaya B. Kolachalama
Abstract
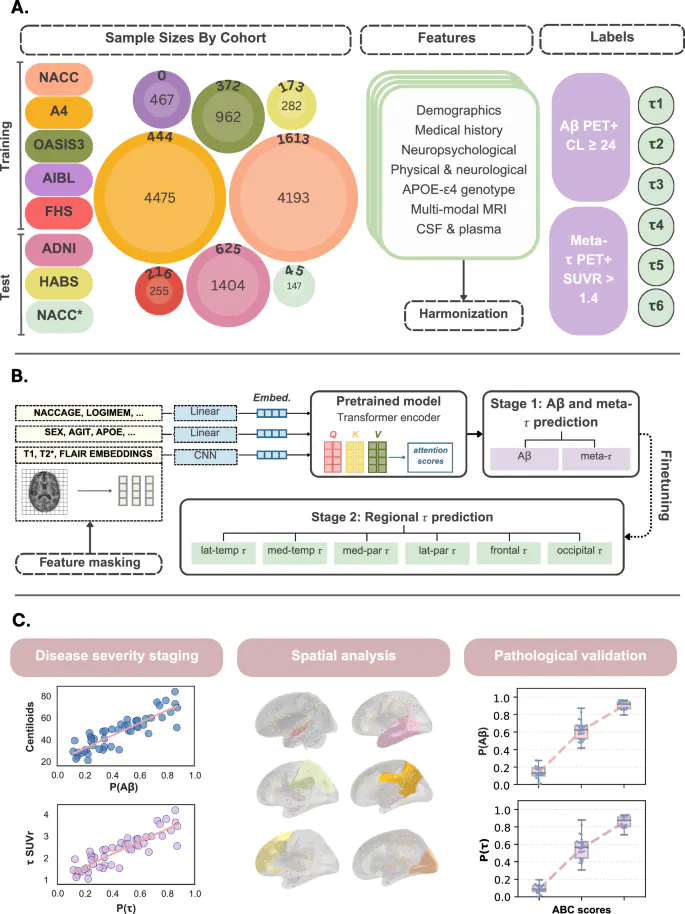
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) diagnosis hinges on detecting amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tau (τ) tangles, typically assessed using PET imaging. While accurate, these modalities are expensive and not widely accessible, limiting their utility in routine clinical practice. Here, we present a multimodal computational framework that integrates data from seven distinct cohorts comprising 12, 185 participants to estimate individual PET profiles using more readily available neurological assessments. Our approach achieved an AUROC of 0.79 and 0.84 in classifying Aβ and τ status, respectively. Predicted PET status was consistent with various biomarker profiles and postmortem pathology, and model-identified regional brain volumes aligned with known spatial patterns of tau deposition. This approach can support scalable pre-screening of candidates for anti-amyloid therapies and clinical trials targeting Aβ and τ, offering a practical alternative to direct PET imaging.
Type
Publication
Nature Communications